The NewGen™ and Saunders Brothers teams at the Third International Summit on Boxwood Challenges, hosted by the American Boxwood Society.
Last month the American Boxwood Society hosted its Third International Summit on Current Boxwood Challenges. Over 140 people heard from researchers and growers from Europe, Canada and the United States who discussed the latest research on Boxwood Blight and the Boxwood Tree Moth. This one-day event was hosted at the National Agricultural Library in Beltsville, Maryland.
Although the Boxwood Tree Moth has not been found in the United States, it has devastated boxwood production in Europe. The morning session of the event began with research on the biology of the moth, determining the invasive pathways that introduced the moth to Europe, concluding that the pest was originally introduced from eastern China to Germany in 2007 and has since spread significantly over Europe. Most of the spread has been from the transport of infected plant material, with some movement through native boxwood forests. The moth was found in the United Kingdom in 2008 and has since spread around the southern parts of the country. Chris Poole, the Chairman of the European Boxwood & Topiary Society, shared management strategies being utilized in the United Kingdom and around Europe against the moth.
The morning session finished with speakers from North America, focusing on what the Canadian industry is doing to monitor and prevent the spread, and how the U.S. can prepare against the moth. First identified in Ontario in October 2018, OMAFRA (similar to U.S. Extension) has diligently been monitoring and treating the pest as it appears. Using many of the same tactics that have been effective in Europe, most infections are low to moderate, with less than 10% considered severe. In the United States, using pheromone traps for detection and diligently spreading the word about this potentially invasive species can aid in catching the moth early. In the event that it is found, there are methods of control already available. Researchers are aware of the pest and are focusing efforts to learn from those already affected in order to prevent the introduction of Boxwood Tree Moth to the United States.
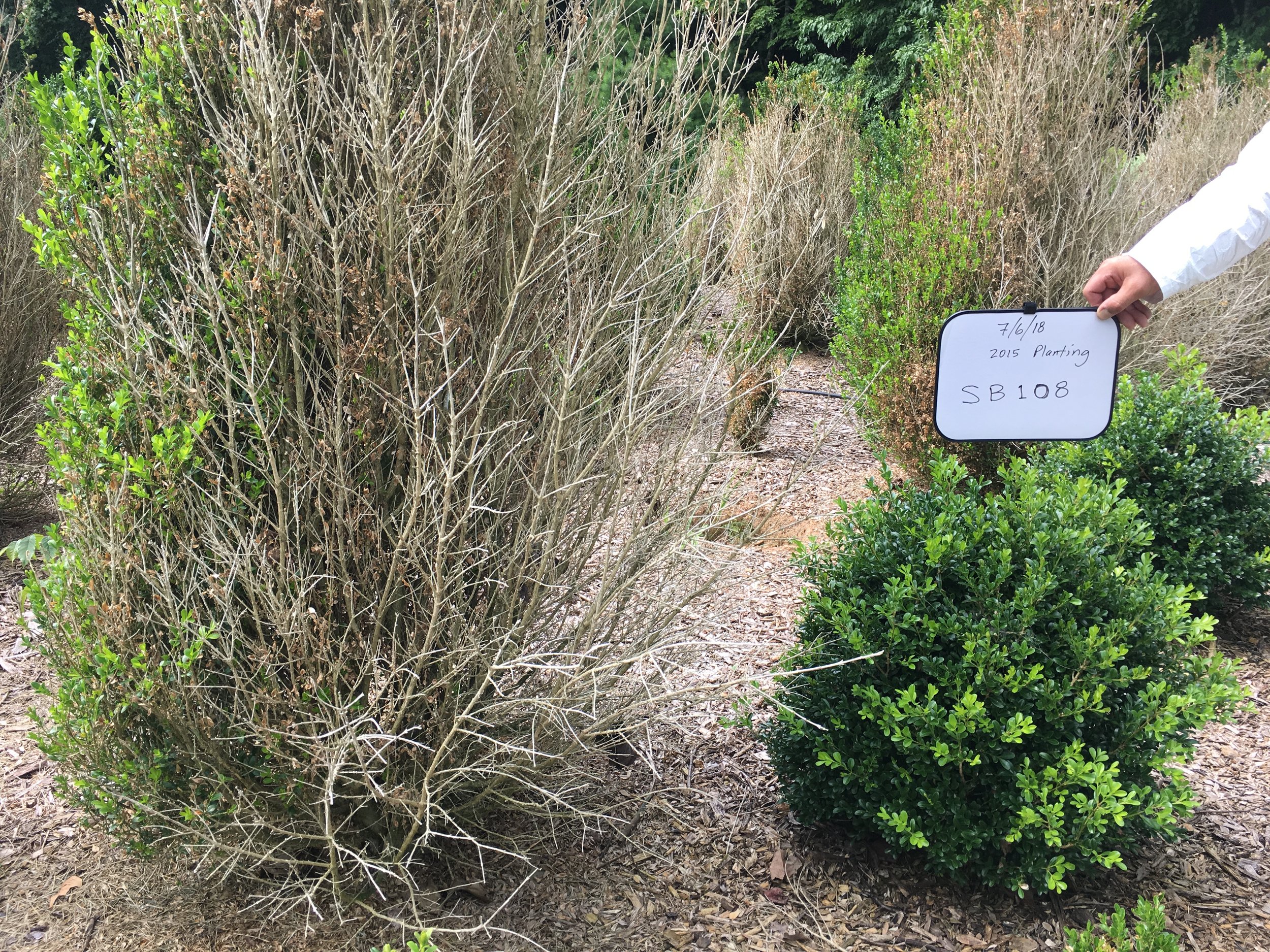
The afternoon focused on Boxwood Blight starting with a recap of what is known about the disease and ways to treat and prevent it. Mary Ann Hansen, who works in the Plant Disease Clinic at Virginia Tech, has many years’ experience identifying Boxwood Blight. She shared information about the biology of the disease, how to identify it, and how to clean it up in the event of an infection. There are many tools available to the public about Boxwood Blight, including the Virginia Boxwood Blight Task force website.
The event finished with several presentations on further research being done around the U.S. There are many projects in the works focused on learning new and effective control strategies. Projects range from breeding programs to biocontrol studies to thermotherapy, all being done at many universities around the U.S. There is still no silver bullet in preventing or treating Boxwood Blight, but the is a light at the end of the tunnel as much of the research proves positive. One of the recent studies showed a decrease of Boxwood Blight lesions by 97% just from adding a layer of mulch. You can read more about that study here. As research continues, we only get more positive that as an industry we can overcome this challenge.
If you’d like to learn more about events like these, check out the American Boxwood Society’s website.